In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most transformative innovations in the digital age. Its potential to revolutionize industries, from finance and healthcare to logistics and voting systems, has captured the attention of businesses, governments, and technologists alike. But what exactly is blockchain technology, and how does it work? In this article, we will dive deep into the fundamentals of blockchain, explain how it works, explore its key features, and discuss its potential applications in various sectors.
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner.
- The technology is immutable, meaning that once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with.
- Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake ensure that transactions are validated and added to the blockchain.
- Blockchain has wide-ranging applications beyond cryptocurrency, including supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems.
- While blockchain is highly secure, it is important to understand that it is not entirely immune to hacking or other security risks.
- As blockchain adoption grows, it is poised to revolutionize many industries by improving transparency, security, and efficiency.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
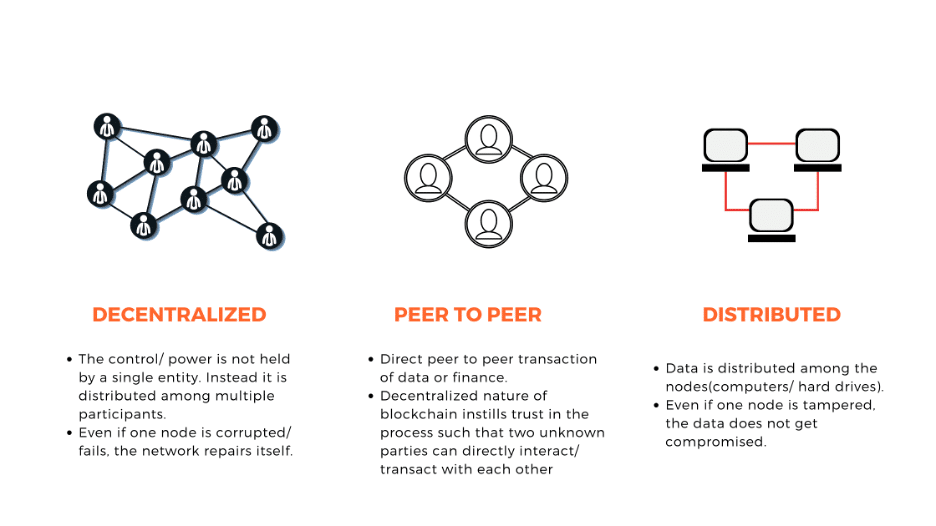
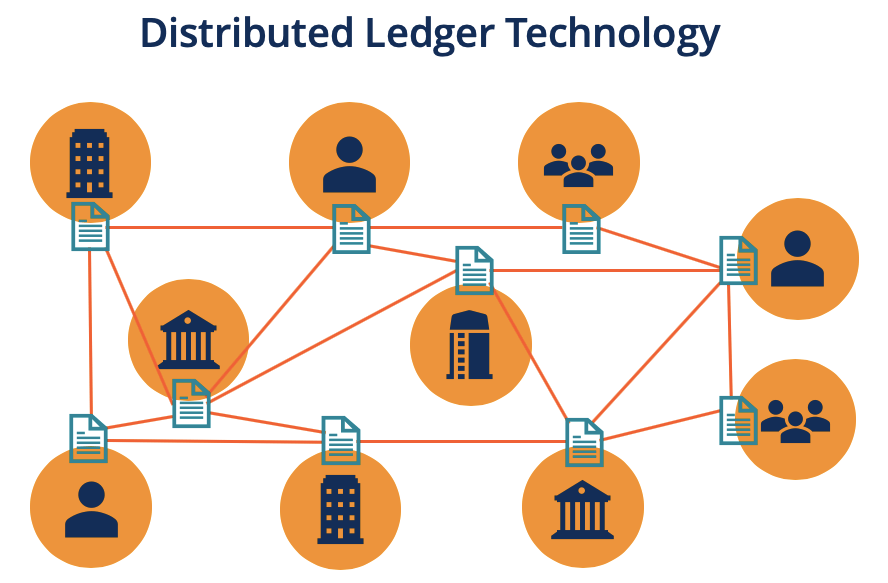
At its core, blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional centralized databases, where a single entity controls the data, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, allowing anyone within the network to validate and record transactions.
A blockchain is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a way that makes it extremely difficult to alter any information without affecting all subsequent blocks. This immutable nature of blockchain ensures security and trust in the system, which is why it is often referred to as a trustless system.
Blockchain technology was initially introduced as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency. However, its potential goes far beyond digital currencies. Today, blockchain is being explored for a wide range of applications, including supply chain management, healthcare, identity verification, and even voting systems.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology

To understand how blockchain works, it is essential to look at some of its key features:
Decentralization
Unlike traditional systems, where data is stored and controlled by a central authority, blockchain operates in a decentralized manner. This means that no single entity controls the data; instead, it is distributed across a network of computers (known as nodes). Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain, and each one can validate transactions. This decentralization ensures that there is no single point of failure, making the system more secure and resistant to tampering.
Immutability
One of the defining characteristics of blockchain technology is immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete. Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, which links the blocks together. If someone attempts to change a block’s data, the hash will no longer match, and the tampered block will be rejected by the network. This feature makes blockchain particularly valuable for applications requiring transparency and trust, such as financial transactions.
Transparency
Blockchain offers transparency because all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that is accessible to everyone on the network. This ensures that all participants can verify the transaction history, making it easier to track assets, monitor processes, and ensure compliance with regulations. While the details of individual transactions are visible, the identity of participants can remain anonymous (or pseudonymous), depending on the type of blockchain.
Security
Blockchain employs advanced cryptography to secure transactions. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one using a cryptographic hash function. Additionally, blockchain networks typically require consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to validate transactions. These mechanisms make it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter the blockchain without gaining control of the majority of the network, which would be extremely difficult and costly.
Consensus Mechanisms
In a blockchain, transactions must be validated before being added to the ledger. This is achieved through consensus mechanisms. These mechanisms ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions. The two most common consensus mechanisms are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): In PoW, nodes (called miners) compete to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process requires significant computational power, making it energy-intensive. Bitcoin, for example, uses PoW.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In PoS, validators (called stakers) are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. PoS is considered more energy-efficient than PoW and is used by blockchains like Ethereum 2.0.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Now that we understand the key features of blockchain, let’s break down how the technology works. At a high level, the process can be described as follows:
Transaction Initiation
The process starts when a participant (a user, company, or system) initiates a transaction. For example, this could be sending cryptocurrency, transferring data, or updating a smart contract.
Transaction Verification
Once the transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to the blockchain network, where nodes (computers) validate the transaction. Validation involves checking the transaction’s authenticity, ensuring the sender has sufficient funds or permissions, and confirming that the transaction complies with the network’s rules.
Transaction Block Creation
Once the transaction is validated, it is bundled together with other transactions into a block. This block is then added to the blockchain in a secure and immutable manner. The block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, linking it to the chain and ensuring that any attempt to alter the data would be immediately detected.
Consensus Mechanism
After the block is created, it needs to be verified by the network through a consensus mechanism. In the case of Proof of Work, miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add the block to the blockchain and is rewarded with cryptocurrency. In Proof of Stake, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked and their past behavior.
Block Addition and Finalization
Once a consensus is reached, the new block is added to the blockchain. At this point, the transaction is considered final and irreversible. The updated blockchain is distributed to all nodes in the network, ensuring that everyone has the same copy of the ledger.
Transaction Completion
After the block is added to the blockchain, the transaction is considered complete, and the recipient can now access the transferred asset or data. The process is complete, and the transaction is recorded on an immutable, decentralized ledger.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is far more than just the backbone of cryptocurrencies. Its decentralized and secure nature makes it applicable to a wide variety of industries. Here are some of the most prominent use cases for blockchain:
Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain technology is in cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies rely on blockchain to securely record transactions, validate ownership, and prevent fraud.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods through a supply chain. With blockchain, all parties in the supply chain, from manufacturers to consumers, can have access to a transparent, real-time ledger of transactions. This can help reduce fraud, improve efficiency, and increase accountability.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain can be used to securely store and share patient data, enabling healthcare providers to access patient records quickly and securely. Blockchain also ensures that patient data is tamper-proof and can only be accessed by authorized individuals.
Voting Systems
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize voting systems by providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to record votes. By using blockchain, governments can ensure that votes are counted accurately and that the system is resistant to fraud.
Identity Verification
Blockchain can be used to create secure digital identities for individuals. By using blockchain, people can have full control over their personal data and share it only with trusted parties, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts run on blockchain platforms like Ethereum and can be used to automate transactions, reduce the need for intermediaries, decentralized and increase trust between parties.
Read More : How Crypto Gaming Is Revolutionizing The Future Of Online Entertainment
How Blockchain Can Revolutionize Supply Chain Management
- Detailed exploration of how blockchain ensures transparency, traceability, and efficiency in supply chains.
- Use cases in industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and retail.
- Benefits such as eliminating fraud, improving product recall processes, and ensuring ethical sourcing.
The Future of Cryptocurrency: Trends to Watch in 2024 and Beyond
- Discuss the growing adoption of cryptocurrency by both businesses and consumers.
- Regulatory challenges and how they will affect the market.
- The impact of digital currencies and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) on traditional financial systems.
- Analysis of new cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based innovations in the space.
How Blockchain Technology Enhances Cybersecurity
- How blockchain’s decentralized nature helps to improve data security and reduce cybercrime.
- Applications in secure data sharing, identity verification, and protecting personal data.
- Key challenges and limitations of blockchain as a cybersecurity tool.
Understanding Smart Contracts: Benefits and Use Cases
- What smart contracts are and how they work.
- Use cases across different industries, including real estate, legal services, finance, and insurance.
- Benefits such as reducing reliance on intermediaries and speeding up transactions.
- Potential drawbacks, including coding errors and the need for widespread adoption.
Blockchain for Healthcare: Transforming Patient Data and Medical Research
- How blockchain can improve healthcare data management, secure medical records, and enhance patient privacy.
- The potential for blockchain in streamlining the drug supply chain and reducing counterfeit drugs.
- Future opportunities for improving medical research collaboration and data sharing.
The Role of Blockchain in Voting Systems: Secure and Transparent Elections
- How blockchain can create tamper-proof voting systems.
- Benefits of blockchain voting, including transparency, security, and accessibility.
- Current and potential challenges, including technological and regulatory hurdles.
- Case studies of blockchain-based voting systems in trials or actual elections.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology represents a groundbreaking shift in how we handle digital information. By offering a secure, decentralized, and transparent way to manage data, it has the potential to revolutionize industries ranging from finance and healthcare to voting and supply chain management.
The key to understanding blockchain lies in its core features: decentralization, immutability, transparency, and security. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, further transforming the digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is blockchain technology in simple terms?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers, making it secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant.
How does blockchain technology work in cryptocurrency?
Blockchain technology works in cryptocurrency by securely recording transactions in a decentralized manner. It ensures that all transactions are validated and stored in an immutable ledger.
What are the advantages of blockchain technology?
The advantages of blockchain include decentralization, transparency, security, immutability, and efficiency in verifying and recording transactions.
Can blockchain be hacked?
While blockchain technology is highly secure, it is not entirely immune to attacks. However, altering the blockchain requires a majority of the network to be compromised, which is extremely difficult and costly.
Is blockchain technology only for cryptocurrencies?
No, blockchain technology has many applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including supply chain management, healthcare, identity verification, and voting systems.
What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract where the terms of the agreement are written into code on a blockchain platform. It automatically enforces the terms once predefined conditions are met.
Why is blockchain technology important?
Blockchain technology is important because it provides a secure, and transparent way to record and validate transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing efficiency.