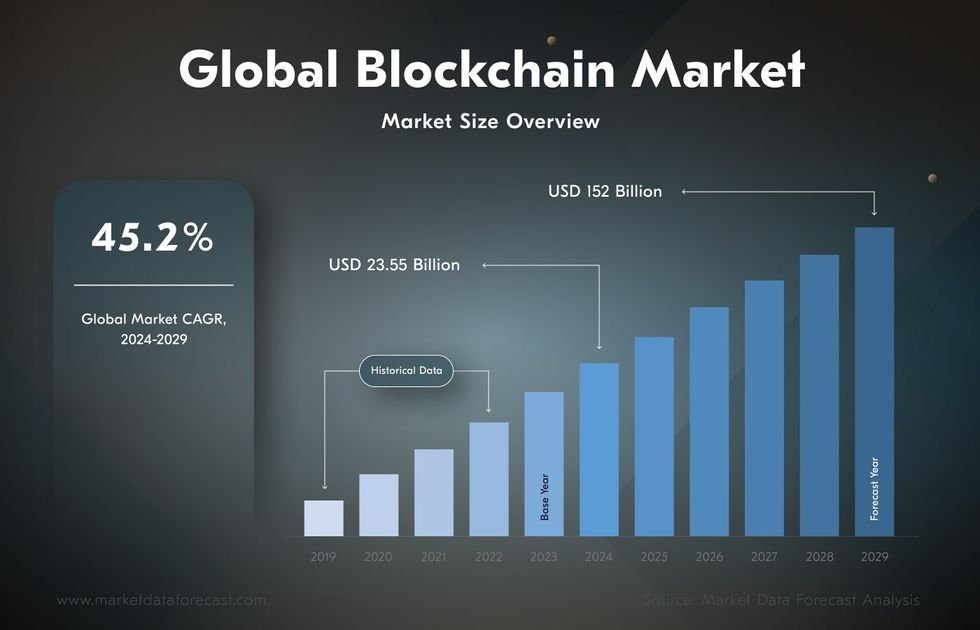
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is one of the most transformative and disruptive innovations in the world of digital technologies today. While blockchain often dominates discussions around DLT, there are several other types of distributed ledgers, each with its own unique characteristics. The technology is poised to revolutionize various industries, including finance, healthcare, supply chain, and government services, by enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security.
In this article, we’ll explore what Distributed Ledger Technology is, how it works, its key benefits, and some of its most prominent use cases. We’ll also dive into the differences between blockchain and other types of DLT, address some frequently asked questions, and highlight key takeaways to help you better understand the technology.
Key Takeaways
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a decentralized system that ensures data integrity, transparency, and security.
- DLT operates through a consensus mechanism where participants agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the ledger.
- Key benefits of DLT include decentralization, transparency, immutability, enhanced security, and reduced costs.
- DLT has numerous use cases, including cryptocurrency, supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, and more.
- Blockchain is the most well-known type of DLT, but other variations such as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) and Hashgraph are gaining traction.
- DLT is poised to revolutionize various industries by improving efficiency, security, and reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Introduction to Distributed Ledger Technology
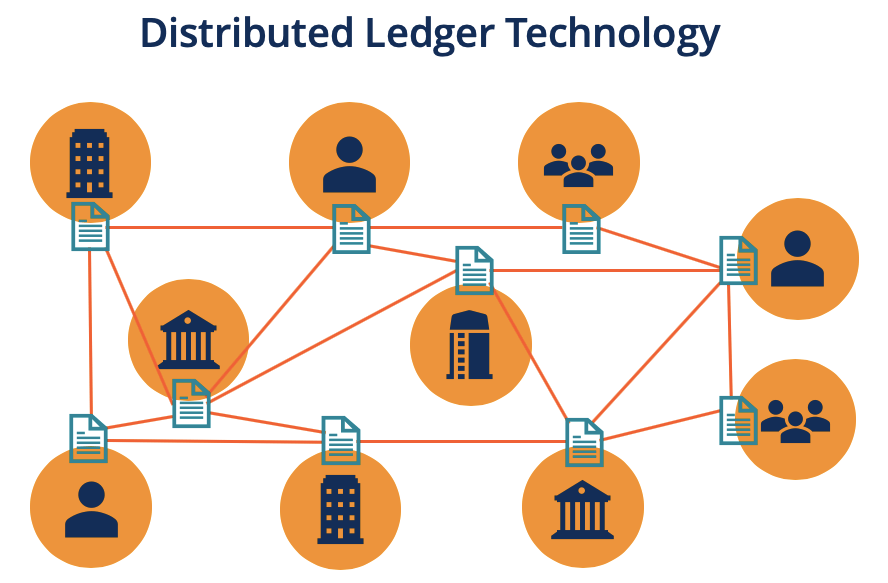
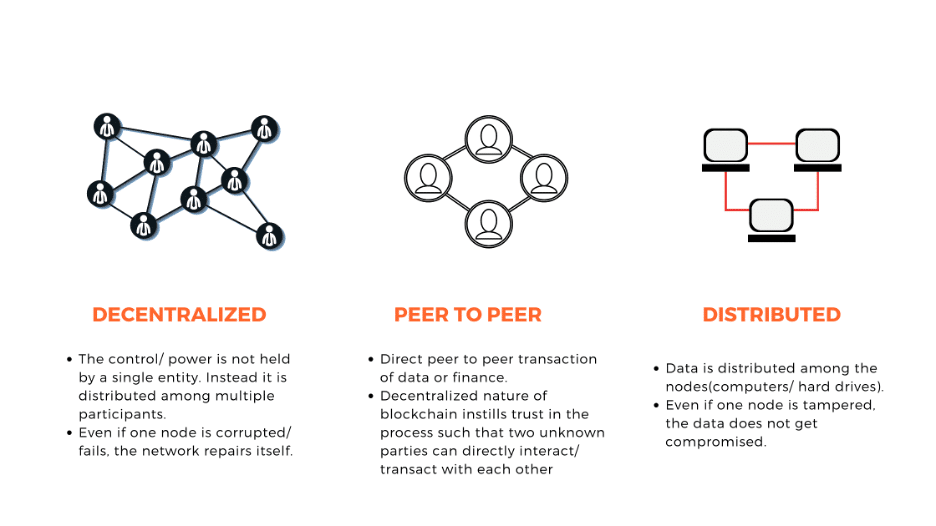
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) refers to a decentralized database or ledger that is shared, replicated, and synchronized across multiple locations or participants. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single entity controls the database, DLT operates on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring that data is stored in multiple places and not dependent on any central authority. This makes DLT highly resilient to tampering, hacking, or data loss.
DLT allows all participants on the network to access and verify the same information in real time. It does so in a way that ensures the accuracy and integrity of the data while enabling quick, secure transactions. DLT is often associated with blockchain, but there are other types of DLT as well, such as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), which is used by some cryptocurrency networks like IOTA.
One of the key features of DLT is immutability—once data is recorded on a distributed ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted without the consensus of the majority of the network participants. This immutability ensures that the data remains accurate, transparent, and trustworthy.
How Does Distributed Ledger Technology Work?

The mechanics of DLT depend on the specific type of ledger being used. However, the general principles remain consistent. Here’s how the basic process typically works:
1. Data Creation
When a new transaction or piece of data is generated, it is broadcast to the network. For example, in a financial transaction, this could be a transfer of funds between two parties.
2. Consensus Mechanism
Before the data can be added to the ledger, the network must agree on its validity. This is where the consensus mechanism comes into play. In some systems, like blockchain, the consensus mechanism might be Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). In other types of DLT, different consensus algorithms may be used.
The consensus mechanism ensures that all participants on the network are in agreement about the accuracy of the data before it is validated and added to the ledger.
3. Data Recording
Once consensus is achieved, the validated data is added to the distributed ledger. In the case of blockchain, this data is recorded in a “block” and linked to the previous block, forming a continuous chain. For other DLT systems, the structure might be different, but the principle remains the same: data is stored across a decentralized network of nodes.
4. Replication and Synchronization
The updated ledger is then replicated across all the nodes in the network, ensuring that every participant has the same information. Since the ledger is decentralized, no single participant has control over it, making it highly secure and transparent.
5. Immutability and Security
Once data is added to the ledger, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be changed or deleted without the consensus of the majority of participants in the network. This characteristic ensures that all data stored on the ledger is trustworthy and tamper-resistant.
Types of Distributed Ledger Technology
While blockchain is the most widely known type of DLT, it is not the only one. There are several other types of distributed ledgers, each with different structures and uses. Some of the key types include:
1. Blockchain
Blockchain is the most popular type of DLT and is best known for supporting cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In a blockchain, data is stored in blocks, and each block is linked to the previous one in a chain. This chain structure ensures that the data is secure and transparent.
2. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
DAG is another type of distributed ledger technology used by networks like IOTA. Unlike blockchain, DAG does not use blocks or miners to validate transactions. Instead, transactions are recorded in a graph structure where each new transaction validates two previous ones. This structure makes DAG more scalable and efficient than blockchain in certain use cases.
3. Holochain
Holochain is a DLT that operates without a global consensus mechanism. Instead, each participant in the network maintains their own chain and validates their own transactions. This approach is designed to be more energy-efficient than blockchain and allows for faster transaction speeds.
4. Hashgraph
Hashgraph is another alternative to blockchain and is designed to be fast, secure, and scalable. Unlike blockchain, which is linear in structure, Hashgraph is based on a directed acyclic graph and uses a consensus algorithm known as the “gossip about gossip” protocol to reach consensus among participants.
5. Tangle
Tangle is a unique form of DLT developed by IOTA. It uses a structure similar to DAG but emphasizes scalability and lightweight transactions. Tangle’s architecture is designed to handle large volumes of small transactions, making it ideal for the Internet of Things (IoT) networks.
Key Benefits of Distributed Ledger Technology
DLT offers a range of advantages over traditional centralized systems. Some of the most notable benefits include:
1. Decentralization
One of the core principles of DLT is decentralization. Unlike traditional systems, which rely on a central authority to verify and store data, DLT is decentralized and distributed across multiple nodes. This ensures that no single participant has control over the data, reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
2. Transparency
Because every participant on the network has access to the same information, DLT enhances transparency. This is particularly useful in industries like supply chain management, where consumers and businesses need to trace the origin and movement of products.
3. Immutability
Once data is added to the distributed ledger, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This makes DLT highly secure and ensures the integrity of the data.
4. Security
DLT employs strong cryptographic techniques to ensure that data is securely transmitted and stored. This makes it difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the data or carry out fraudulent transactions.
5. Efficiency
DLT can streamline processes by eliminating the need for intermediaries. This leads to faster transactions, reduced costs, and improved efficiency, especially in areas like payments, supply chain management, and cross-border transactions.
6. Resilience
Since data is replicated across multiple nodes, DLT is highly resilient to cyberattacks, system failures, and data breaches. If one node goes offline, the data is still accessible through other nodes on the network.
7. Cost-Effectiveness
By eliminating intermediaries and reducing the need for centralized infrastructure, DLT can lower transaction fees and operational costs. This is particularly valuable in industries like finance and banking, where intermediaries often charge high fees.
Use Cases of Distributed Ledger Technology
DLT has a broad range of applications across various industries. Below are some of the most impactful use cases:
1. Cryptocurrency and Payments
DLT, particularly blockchain, is the foundation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. DLT is also used in cross-border payments, where it can reduce transaction fees and speed up processing times.
2. Supply Chain Management
DLT enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains by allowing stakeholders to track the movement of goods in real time. Blockchain can ensure the authenticity of products, such as luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, or food, by providing an immutable record of each transaction.
3. Healthcare
DLT can be used to securely store and share patient medical records. By using a decentralized network, healthcare providers can access accurate and up-to-date patient data, improving coordination of care and reducing the risk of errors.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain and other forms of DLT are being explored as solutions for secure and transparent voting systems. With DLT, votes can be recorded in an immutable ledger, reducing the risk of election fraud and enhancing public trust in election outcomes.
5. Intellectual Property Protection
DLT can help manage intellectual property rights by securely recording the ownership and provenance of digital assets like music, art, and patents. It can ensure that creators receive fair compensation for the use of their work.
6. Smart Contracts
DLT enables the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. These contracts automatically execute when certain conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and improving efficiency in industries like real estate, insurance, and legal services.
7. Insurance
DLT can streamline the insurance process by automating claims management and reducing fraud. Smart contracts can be used to automatically process claims when predefined conditions are met, enhancing trust and transparency in the industry.
Read More : What Are the Most Impactful Blockchain Use Cases in 2024?
Conclusion
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is one of the most promising innovations of the digital age. Its ability to offer decentralized, transparent, and secure systems makes it an ideal solution for a wide range of industries, from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and voting systems. As we move into 2024 and beyond, DLT will continue to disrupt traditional systems, improving efficiency, security, and transparency in countless applications.
FAQs
What is the difference between blockchain and DLT?
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology, but DLT encompasses a broader range of technologies, including blockchain, Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), and others like Hashgraph and Holochain.
How does DLT ensure security?
DLT ensures security through cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms that validate transactions and make the data immutable. This makes it difficult for malicious actors to alter the data.
Is DLT only used for cryptocurrencies?
No, DLT has applications across various industries, including supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, insurance, and more.
What are the main advantages of DLT over traditional systems?
DLT offers decentralization, transparency, immutability, enhanced security, and cost-effectiveness. It eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of data tampering.
How does consensus work in DLT?
Consensus mechanisms ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of a transaction before it is added to the ledger. Examples of consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Can DLT be used in government systems?
Yes, DLT has the potential to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in government systems, especially for applications like voting, public records management, and identity verification.
What is a smart contract in DLT?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract where the terms are coded into the blockchain or DLT system. These contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.